Basidiomycota Life Cycle . The first stage is represented by the primary mycelium or homokaryon (b) which is formed by the germination of a basidiospore (a). The lifecycle of basidiomycetes includes sexual and asexual reproduction (figure 2).
Neurospora lifecycle from www.mun.ca
Turn your attention to the basidiomycete life cycle in figure 5. Many basidiomycota produce basidia on. Nested within the kingdom fungi, the basidiomycota spend most of their life cycle underground before.
Neurospora lifecycle
The primary mycelium often produces oidia. The division of fungi known as the club fungi, basidiomycota, includes some of the most familiar fungi. The lifecycle of basidiomycetes includes sexual and asexual reproduction (figure 2). The following description of the characteristics of basidiomycota traces the life cycle of a typical species, beginning at the site of meiosis.
Source: www.pinterest.es
Check Details
In basidiomycetes, the sexual cycle typically involves fusion of genetically distinct homokaryotic hyphae or haploid yeast cells to produce a dikaryon, in which the two haploid parental nuclei are replicated in a coordinated fashion without fusion during hyphal elongation, usually involving the formation of clamp connections (i.e. The fused hyphae containing haploid nuclei from two individuals is heterokaryotic. Many basidiomycota.
Source: web.augsburg.edu
Check Details
The following description of the characteristics of basidiomycota traces the life cycle of a typical species, beginning at the site of meiosis. The fused hyphae containing haploid nuclei from two individuals is heterokaryotic. The mycelium of basidiomycetes passes through three distinct stages namely, the primary, the secondary and the tertiary before the fungus completes its life cycle. One of the.
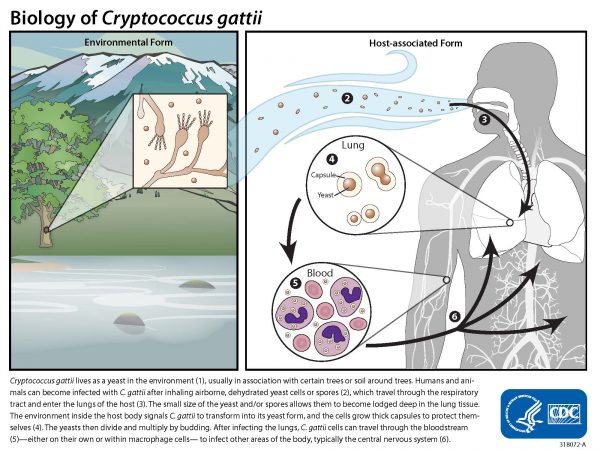
Source: www.cdc.gov
Check Details
The mycelium of basidiomycetes passes through three distinct stages namely, the primary, the secondary and the tertiary before the fungus completes its life cycle. Basidiomycota characterized by having meiospores called basidiospores. The basidium is the cell in which karyogamy (nuclear fusion) and meiosis occur, and on which haploid basidiospores are formed (basidia are not produced by asexual basidiomycota). Nested within.
Source: pediaa.com
Check Details
Basidiomycota characterized by having meiospores called basidiospores. The mycelium of basidiomycetes passes through three distinct stages namely, the primary, the secondary and the tertiary before the fungus completes its life cycle. Furthermore, both their life cycle comprises three stages: The mycelium of basidiomycetes passes through three distinct stages namely, the primary, the secondary and the tertiary before the fungus completes.
Source: web.augsburg.edu
Check Details
The mycelium of basidiomycetes passes through three distinct stages namely, the primary, the secondary and the tertiary before the fungus completes its life cycle. One of the most important stages in this life cycle is reproduction. Although some basidiomycetes produce asexual spores, asexual reproduction is far more common in the phylum ascomycota. The first stage is represented by the primary.
Source: www.mun.ca
Check Details
In basidiomycetes, the sexual cycle typically involves fusion of genetically distinct homokaryotic hyphae or haploid yeast cells to produce a dikaryon, in which the two haploid parental nuclei are replicated in a coordinated fashion without fusion during hyphal elongation, usually involving the formation of clamp connections (i.e. The following description of the characteristics of basidiomycota traces the life cycle of.
Source: bio1903.nicerweb.com
Check Details
The mycelium of basidiomycetes passes through three distinct stages namely, the primary, the secondary and the tertiary before the fungus completes its life cycle. The yeast states provide one approach to studying the relationships of dimorphic fungi, including determining relationships between anamorphic yeasts and their teleomorphs. Turn your attention to the basidiomycete life cycle in figure 5. The fusion of.